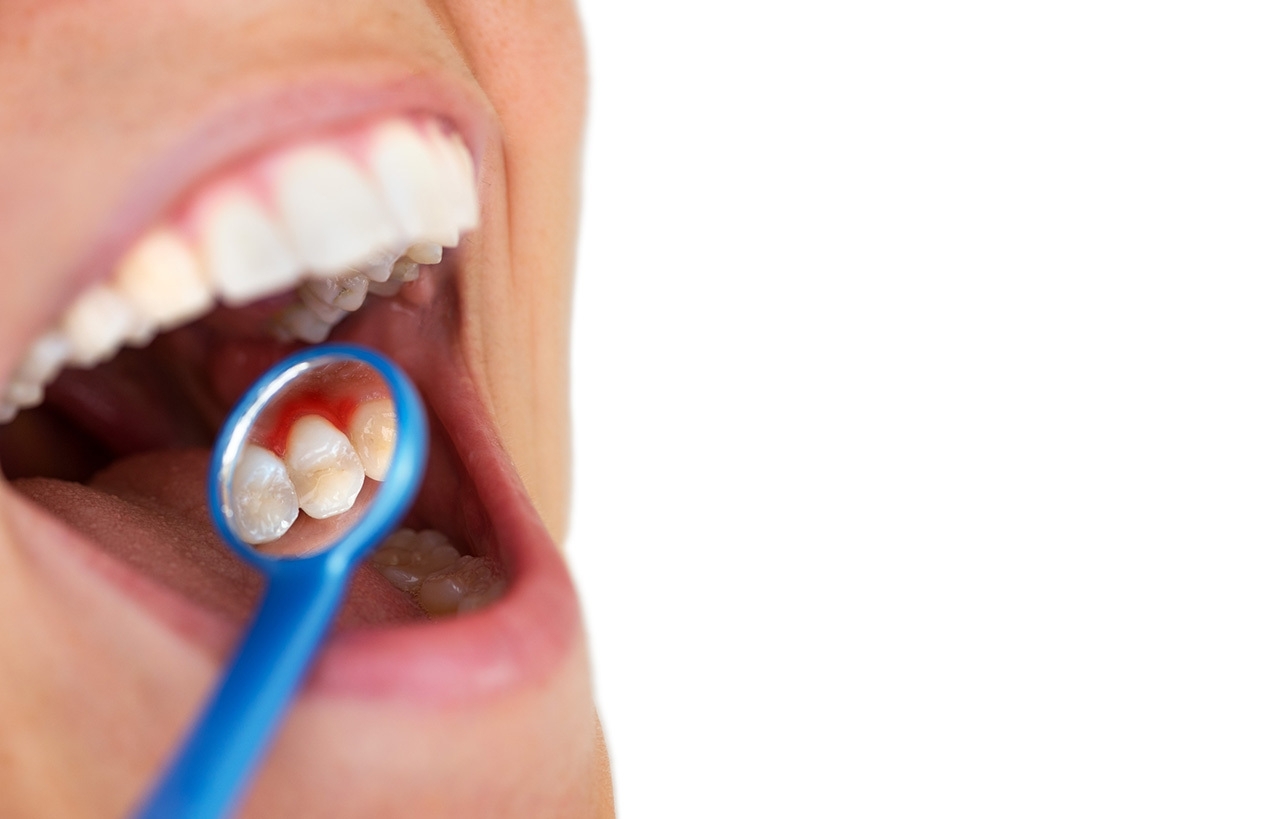
Clinically, gingivitis is manifested, among other things, by bleeding gums which at times is intense. As a nosological entity it is curable and completely reversible with treatment and proper oral hygiene.
What causes gingivitis?
Poor oral hygiene and non-attendance at the dental clinic for the removal of dental plaque every 6 months are the main causative factors. At the same time, hormonal disorders, such as adolescence, pregnancy or menopause, cause gingivitis. At the same time, taking certain medications such as contraceptives or the presence of systemic diseases such as diabetes have been implicated in gingivitis.
What are the symptoms of gingivitis?
The disease is clinically manifested by abnormal swelling of the gums, bleeding, and bad breath. If the gingivitis is left untreated then it turns into periodontitis and in the final stages leads to tooth loss. If treated early the disease is completely reversible.
How is gingivitis treated?
First, the teeth are cleaned and the necessary oral hygiene instructions are given. In the second phase, gingivitis is treated at 4 visits per quarter under local anaesthesia.
Essentially, a thorough cleaning of our teeth is followed on each side and each area is irradiated with a soft tissue laser such as a diode or CTP laser. Lasers have a perfect application in this disease since they kill germs. It is recommended that the patient be re-examined for the disease every 6 months.
What factors predispose to "gingivitis"
Failure to follow the rules of oral hygiene that include brushing after each meal. Flossing or flossing daily, cleaning the tongue and using mouthwash lead to gingivitis. Crooked teeth are not easy to clean and patients are at risk for gingivitis. Taking certain medications or some systemic diseases cause gingivitis in the teeth.
Does gingivitis cause pain?
Gingivitis does not hurt like a tooth, but bleeding in the mouth should make the patient go to the dentist.
Is gingivitis easily treated?
Once the disease is diagnosed in the early stages, it is curable and completely treatable. If we delay the treatment, it turns into a stage and turns into periodontitis where it is more difficult to treat and sometimes untreatable.


 back to top
back to top